Daylight PDT
Effectively treating actinic keratosis and sun-damaged skin
Everything at a glance
- Treatment duration: 20-30 minutes
- Anesthesia: Injection with local anesthetic
- Aftercare: Avoid direct sunlight and cosmetic creams for the first 48 hours after treatment | Treated areas should not be exposed to direct sunlight for the next 3 months
- Sociability: redness 2 days after treatment (similar to sunburn) | crust formation over 10 to 14 days | then fresh skin appears
- Visibility of the results: After the crusts have fallen off, fresh, new skin can be seen, which may still be reddened for a few weeks - rough areas should be significantly reduced or completely gone. A follow-up treatment may be necessary after 4 weeks (depending on the depth and extent of the actinic keratosis).
- Durability of the results: You can expect long-term results
Tips for immediately after treatment
After the treatment in my practice, the patient should immediately go outside, where he/she should spend the next two hours. The optimum conditions for this are at least 10 degrees, preferably from March to October. Afterwards, it is recommended to go home to wash off the cream residue with lukewarm water and apply the prescribed ointment (twice daily/7 days).
What is photodynamic therapy with daylight?
Photodynamic therapy with daylight (daylight PDT) is a special form of light therapy that is used to treat superficial tumors such as actinic keratosis. A light-sensitized substance is applied to the tumour tissue. This substance accumulates 10 times more in the tumor cells compared to normal skin.
After the application time, the affected areas of skin are exposed to daylight for 2 hours. This leads to the substance being activated and the tumor cells being rejected and destroyed in a targeted manner.
The final result is seen after about 3 months. As a rule, the success of daylight PDT lasts for several years. However, this depends on your lifestyle and, above all, how often you expose yourself to the sun.
BEFORE-AFTER results
BEFORE
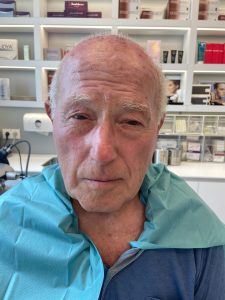
AFTER

When exactly does daylight PDT help?
Damage caused by UV radiation years ago often only becomes apparent after a long delay. They therefore only become noticeable on the surface of the skin much later, even if you no longer expose yourself to strong sunlight or actively protect yourself from it in subsequent years.
The skin changes mainly appear on the so-called sun terraces of the face (lower lip, upper ear area, nose, forehead, bald head). Shoulders, décolleté, forearms and the backs of the hands are also affected. You can recognize such sun damage by the fact that the skin feels scaly, rough or crusty. In this case, it is very likely that you are affected by actinic keratosis (AK).
How does a daylight PDT work?
- Apply a "chemical" sunscreen with a high sun protection factor (50+) in the morning, which should be left on for at least 15 minutes.
- Disinfection followed by injection of the areas to be treated with a local anesthetic and pre-treatment of these areas with the fractionated CO2 laser.
- Apply the ALA cream in a layer about one millimeter thick with a glove or spatula.
- Within 30 minutes, the treated person should go outside for approx. 2 hours (stay in partial shade, at a temperature of at least +10 °C, from March to October).
- Wash off the cream residue with lukewarm water.
- Application of the prescribed ointment (twice daily/7 days).
- Application of light protection products.
- Avoid the sun for the next 48 hours.
- After 4 weeks, a clinical check-up is carried out in the practice and, if necessary, a second treatment.
Actinic keratosis as a harbinger of white skin cancer
The tricky thing about actinic keratosis is that those affected rarely show any symptoms. However, actinic keratoses do not heal on their own and are a precursor to white skin cancer. If left untreated, they can develop into a malignant spiky cancer after a certain time, which can also metastasize. If an actinic keratosis is treated dermatologically in good time, its transformation into white cancer (squamous cell carcinoma) can be prevented.
Despite countless alternative types of treatment, photodynamic therapy with daylight has proved particularly successful.
Frequency and signs of actinic keratosis
Actinic keratoses are the third most common reason why patients consult a dermatologist. They are also the most common precursor to white skin cancer. This in turn is the most common form of malignant skin tumor and occurs in around 328 out of every 100,000 people in Germany every year.
Because actinic keratoses are the result of long-term exposure to UV radiation, they are particularly common in older people. Patients with immunosuppression are affected even more frequently. Across Europe, it is estimated that every second person over the age of 60 has at least one skin change of this kind. However, it is increasingly common in young people who are frequently exposed to the sun either privately or professionally.
Actinic keratoses usually begin with reddish-brown, reddish or skin-colored areas with whitish, light scaling. This keratinization or scaling increases over time, which is why the skin feels increasingly hard and rough. The oval or round areas often increase in size from just a few millimeters to several centimeters. The outlines can be both sharply defined and irregular.
Comparison between daylight PDT and conventional red light PDT
Until now, white skin cancer has often been treated with conventional PDT, which uses strong red radiation . Although this treatment also proves to be extremely effective, it is painful due to the absorption of creams containing aminolevulinic acid (ALA).
In comparison, daylight PDT offers the same results, but causes hardly any pain. As the irradiation begins immediately after the cream is applied, the ALA substance is consumed by the sunlight immediately after penetrating the cells before it can reach the nerve endings.
The gentle photodynamic therapy with daylight also has the advantage that it can be carried out repeatedly without damaging healthy body tissue. In addition to the treatment and prevention of skin cancer, daylight PDT is also an alternative treatment for other tumors such as superficial basal cell carcinomas or Bowen’s disease. PDT is also used for skin rejuvenation.
It can be treated in various ways, but photodynamic therapy with daylight has proved particularly effective in recent years!
Important FAQs on daylight PDT
What should you consider before a daylight PDT?
Before carrying out the daylight PDT, apply SPF 50 to all areas to be treated in the morning.